遍历 DOM 树
题目
写一个函数遍历 DOM 树,分别用深度优先和广度优先
PS:注意回顾 “Node 和 Element 和区别”
深度优先 vs 广度优先
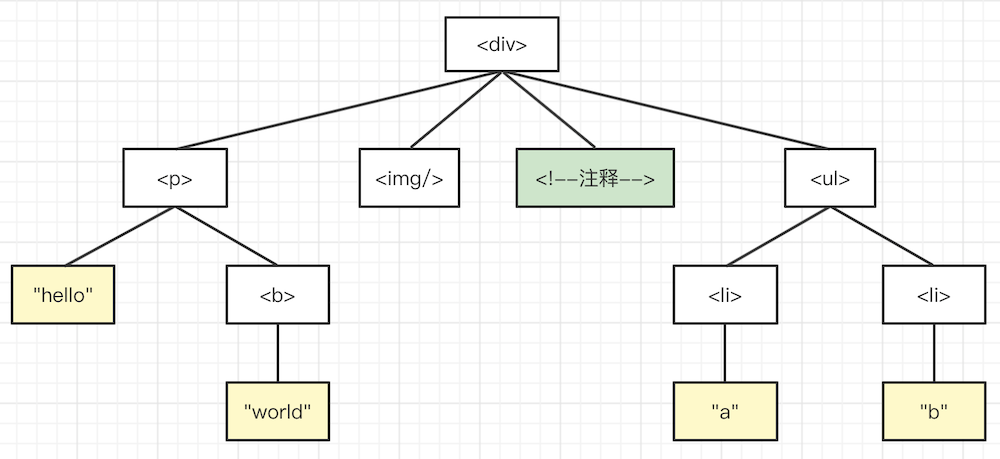
深度优先的结果 <div> <p> "hello" <b> "world" <img> 注释 <ul> <li> "a" <li> "b"
广度优先的结果 <div> <p> <img> 注释 <ul> "hello" <b> <li> <li> "world" "a" "b"
深度优先
一般通过递归实现,代码参考 dom-traverse.ts
广度优先
一般通过队列实现,代码参考 dom-traverse.ts
解答
- 深度优先,递归
- 广度优先,队列
连环问:深度优先可以不用递归吗?
深度优先遍历,可以使用栈代替递归,递归本质上就是栈。代码参考 dom-traverse.ts
递归和非递归哪个更好?
- 递归逻辑更加清晰,但容易出现
stack overflow错误(可使用尾递归,编译器有优化) - 非递归效率更高,但使用栈,逻辑稍微复杂一些
参考
ts
//dom-traverse.ts
/**
* 访问节点
* @param n node
*/
function visitNode(n: Node) {
if (n instanceof Comment) {
// 注释
console.info('Comment node ---', n.textContent)
}
if (n instanceof Text) {
// 文本
const t = n.textContent?.trim()
if (t) {
console.info('Text node ---', t)
}
}
if (n instanceof HTMLElement) {
// element
console.info('Element node ---', `<${n.tagName.toLowerCase()}>`)
}
}
/**
* 深度优先遍历
* @param root dom node
*/
function depthFirstTraverse1(root: Node) {
visitNode(root)
const childNodes = root.childNodes // .childNodes 和 .children 不一样
if (childNodes.length) {
childNodes.forEach(child => {
depthFirstTraverse1(child) // 递归
})
}
}
/**
* 深度优先遍历
* @param root dom node
*/
function depthFirstTraverse2(root: Node) {
const stack: Node[] = []
// 根节点压栈
stack.push(root)
while (stack.length > 0) {
const curNode = stack.pop() // 出栈
if (curNode == null) break
visitNode(curNode)
// 子节点压栈
const childNodes = curNode.childNodes
if (childNodes.length > 0) {
// reverse 反顺序压栈
Array.from(childNodes).reverse().forEach(child => stack.push(child))
}
}
}
/**
* 广度优先遍历
* @param root dom node
*/
function breadthFirstTraverse(root: Node) {
const queue: Node[] = [] // 数组 vs 链表
// 根节点入队列
queue.unshift(root)
while (queue.length > 0) {
const curNode = queue.pop()
if (curNode == null) break
visitNode(curNode)
// 子节点入队
const childNodes = curNode.childNodes
if (childNodes.length) {
childNodes.forEach(child => queue.unshift(child))
}
}
}
const box = document.getElementById('box')
if (box == null) throw new Error('box is null')
depthFirstTraverse2(box)